星空app:205304-87-6
| Name | Tubulysin B |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
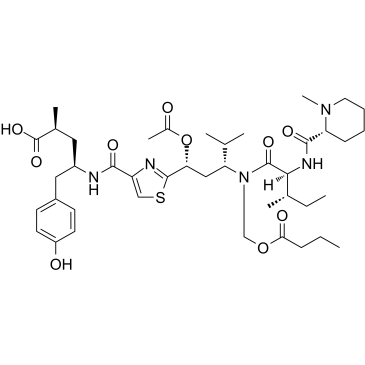
(2S,4R)-4-[({2-[(1R,3R)-1-Acetoxy-3-{[(butyryloxy)methyl](N-{[(2R)-1-methyl-2-piperidinyl]carbonyl}-L-isoleucyl)amino}-4-methylpentyl]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}carbonyl)amino]-5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpentanoic acid
Tubulysin B Pentanoic acid, 4-[[[2-[(1R,3R)-1-(acetyloxy)-4-methyl-3-[[(2S,3S)-3-methyl-2-[[[(2R)-1-methyl-2-piperidinyl]carbonyl]amino]-1-oxopentyl][(1-oxobutoxy)methyl]amino]pentyl]-4-thiazolyl]carbonyl]amino]-5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methyl-, (2S,4R)- |
| Description | Tubulysin B is a highly cytotoxic peptide and potent microtubule destabilizing agents isolated from the myxobacteria Archangium geophyra and Angiococcus disciformis. Tubulysin B has IC50 values in the picomolar range against many cancer cell lines, including those with multidrug resistant properties[1].Tubulysin B is a cytotoxic activity tubulysin which inhibits tubulin polymerization and leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Tubulysin B has IC50s of 0.6 and 0.9 nM against KB and A549 tumors cell lines, respectively. |
| References |
[1]. Leamon CP, et al. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen-Specific Antitumor Activity of a Self-Immolative Tubulysin Conjugate. Bioconjug Chem. 2019 Jun 19;30(6):1805-1813. [2]. Vlahov IR, et al. Acid mediated formation of an N-acyliminium ion from tubulysins: a new methodology for the synthesis of natural tubulysins and their analogs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Nov 15;21(22):6778-81. |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 978.0±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C42H63N5O10S |
| Molecular Weight | 830.042 |
| Flash Point | 545.3±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 829.429565 |
| LogP | 5.78 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.552 |